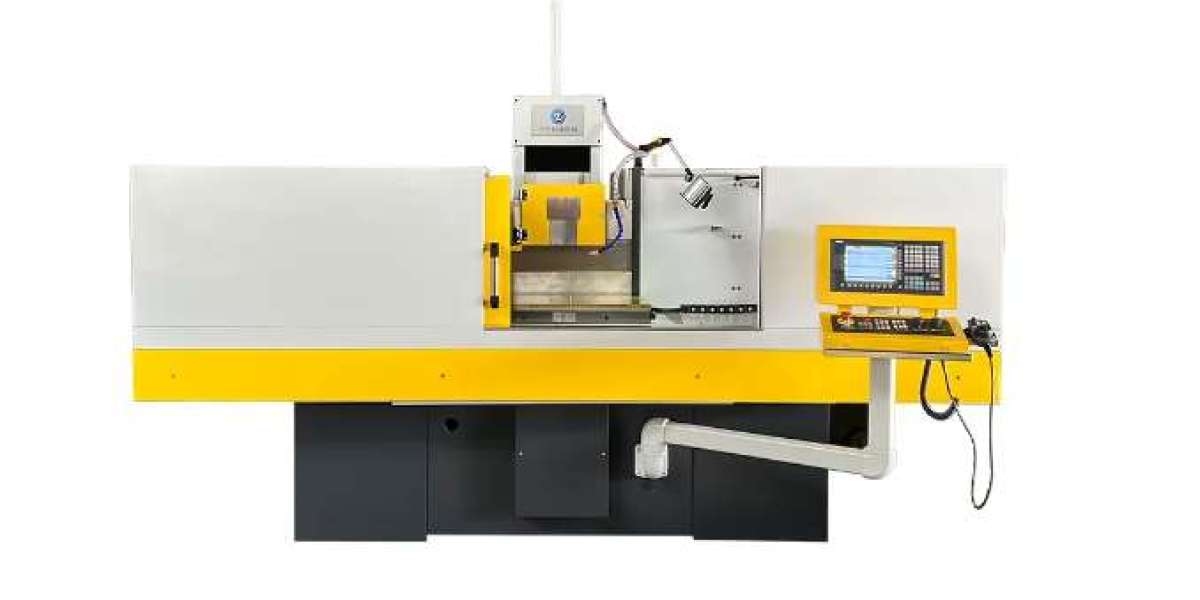
In the world of manufacturing and precision engineering, the 3 axis CNC surface grinder is a vital piece of equipment. It is designed to provide high-precision surface grinding for a variety of materials. In the blog post, Nantong Zode will share how to use 3 axis CNC surface grinder efficiently, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of both the machine and the workpieces.
Understanding the 3 Axis CNC Surface Grinder for sale
Before diving into the operational aspects, it's essential to understand the basic components and functionality of a 3 axis CNC surface grinder:
X-Axis: Horizontal movement of the grinding wheel or workpiece.
Y-Axis: Vertical movement, allowing for depth control.
Z-Axis: Controls the infeed or the distance the grinding wheel moves into the workpiece.
Key Components
Grinding Wheel: The abrasive tool that performs the grinding operation.
Workhead: The part of the machine that holds the grinding wheel.
Control System: The CNC interface that allows for programming and control of the machine's movements.
Dresser: A device used to true and dress the grinding wheel, maintaining its shape and abrasiveness.
Preparing for Operation
Safety First
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear safety glasses, ear protection, and appropriate work clothing.
Machine Inspection: Check for any loose parts, debris, or signs of wear before starting.
Setting Up the Machine
Calibration: Ensure the machine is calibrated according to the manufacturer's specifications.
Tooling: Select the appropriate grinding wheel for the material and desired finish.
Workholding: Secure the workpiece in a vise or magnetic chuck, ensuring it is stable and properly aligned.

Programming the CNC
Understanding CNC Codes
Familiarize yourself with G-codes and M-codes, which are used to control the machine's movements and functions.
G-Codes: Control linear and circular interpolation, tool paths, and positioning.
M-Codes: Control miscellaneous functions like tool changes, coolant, and program stops.
Creating a Program
Define Workpiece Dimensions: Input the size and shape of the workpiece.
Tool Path Planning: Plan the path the grinding wheel will take to achieve the desired surface finish.
Feed Rates and Speeds: Set appropriate feed rates and spindle speeds for the material and operation.
Simulation
Dry Run: Perform a simulation to check for any potential errors in the program.
Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments based on the simulation results.
Operating the 3 axis CNC Surface Grinder
Starting the Machine
Power On: Turn on the machine and allow it to warm up.
Load Program: Load the CNC program into the control system.
Monitoring the Operation
Visual Inspection: Continuously monitor the grinding process for any signs of issues.
Audio Cues: Listen for any unusual sounds that may indicate a problem.
Making Adjustments
Dressing the Wheel: Periodically dress the grinding wheel to maintain its profile and sharpness.
Workpiece Adjustments: Make minor adjustments to the workpiece position if necessary.
Finishing and Inspection
Cool Down: Allow the machine and workpiece to cool after the operation.
Inspection: Check the workpiece for dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Maintenance
Cleanliness: Keep the machine and surrounding area clean.
Lubrication: Regularly lubricate moving parts as per the manufacturer's guidelines.
Filter Checks: Check and replace filters as needed to maintain airflow and coolant quality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Vibration: Check for imbalances in the grinding wheel or workpiece.
Surface Finish Issues: Inspect the grinding wheel for wear and dress as necessary.
Machine Errors: Consult the machine's error log and manual for guidance on resolving issues.
Advanced Techniques
Adaptive Control
Sensor Integration: Use sensors to monitor and adjust the grinding process in real-time.
Feedback Systems: Implement feedback systems to improve accuracy and consistency.
Custom Tool Paths
CAD/CAM Integration: Use CAD/CAM software to create custom tool paths for complex workpieces.
Programming Software: Utilize advanced programming software for more complex CNC operations.
Conclusion
Efficient use of a 3 axis CNC surface grinder requires a combination of understanding the machine, proper setup, careful programming, attentive operation, and regular maintenance. By following the guidelines outlined in this blog post, you can ensure that your CNC surface grinder operates at peak efficiency, delivering high-quality results with minimal downtime.