In the realm of wastewater management, progressive cavity pumps play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient handling and reliable performance. These pumps, specifically designed for the challenges posed by sewage and wastewater applications, offer unique advantages that make them indispensable in various industrial and municipal settings. This comprehensive guide explores the technology behind progressive cavity pumps, their applications in wastewater management and their key benefits.
Introduction to Progressive Cavity Pumps
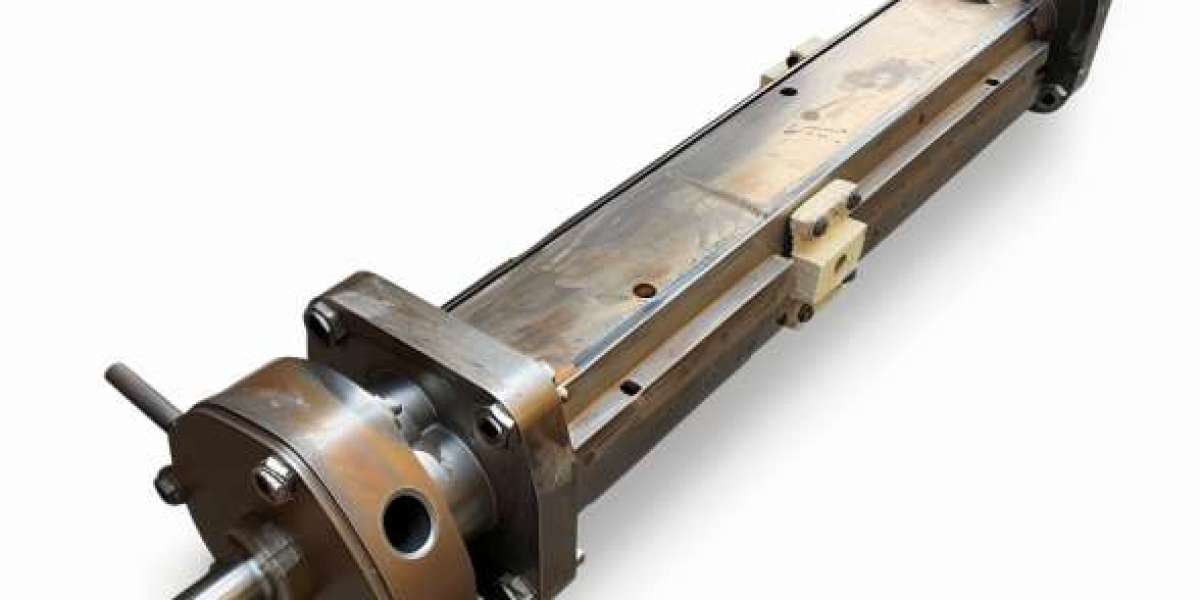
Progressive cavity pumps (PCPs), also known as helical rotor pumps or eccentric screw pumps, are positive displacement pumps that operate on the principle of transferring fluids through a sequence of small, fixed-shape cavities. These pumps are characterized by a helical rotor, which rotates eccentrically within a stator. This rotation creates a progressing cavity between the rotor and the stator, resulting in the movement of fluid from the suction side to the discharge side.
Key Components of a Progressive Cavity Pump:
Rotor: Typically made of stainless steel or other durable materials, the rotor is the rotating component of the pump. Its helical shape interacts with the stator to create a pumping action.
Stator: The stator surrounds the rotor and is usually made of an elastomeric or rubber material. It has a double helix shape that matches the rotor, forming cavities that progress from suction to discharge.
Drive: Provides the mechanical power to rotate the rotor. It can be electric motor-driven, hydraulic, or pneumatic, depending on the application requirements.
Seals and Bearings: Critical for maintaining pump efficiency and preventing leakage, seals and bearings ensure smooth operation and longevity of the pump.
Applications of Progressive Cavity Pumps in Wastewater Management
Progressive cavity pumps are extensively used in the handling of sewage and wastewater due to their ability to handle viscous fluids, solids-laden slurries, and shear-sensitive materials. Their robust design and gentle pumping action make them suitable for various applications within wastewater treatment plants and industrial processes.
Common Applications Include:
Primary Sludge Transfer: PCPs efficiently transfer primary sludge from sedimentation tanks to further processing stages.
Waste Activated Sludge (WAS) Pumping: Used for transporting WAS from biological treatment units to sludge processing facilities.
Chemical Dosing: Precise dosing of chemicals in wastewater treatment processes to optimize treatment efficiency.
Digester Feed: Feeding digester tanks with thickened sludge for anaerobic digestion processes.
Return Activated Sludge (RAS) Pumping: Returning treated sludge from clarifiers back to the biological reactors for continuous treatment.
Filter Press Feeding: PCPs are employed in feeding slurry to filter presses for dewatering purposes.
Advantages of Progressive Cavity Pumps in Wastewater Applications
Progressive cavity pumps offer several advantages that make them ideal for handling progressive cavity pump sewage and wastewater:
Handling Viscous Fluids: PCPs can effectively handle fluids with high viscosity, including sludges and slurries, without losing pumping efficiency.
Solids Handling Capability: They can handle solids up to a certain size without clogging, thanks to their gentle pumping action and large cavities.
Shear-Sensitive Materials: Ideal for pumping materials that are sensitive to shear forces, as the pumping action is gentle and non-aggressive.
Self-Priming: PCPs are capable of self-priming, which is advantageous in applications where priming may be challenging or impractical.
Versatility: They can pump fluids containing abrasive particles and various chemicals commonly found in wastewater streams.
Energy Efficiency: PCPs offer high energy efficiency due to their positive displacement nature, operating at lower speeds compared to centrifugal pumps.
Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and simple maintenance requirements, PCPs offer reduced downtime and lower lifecycle costs.