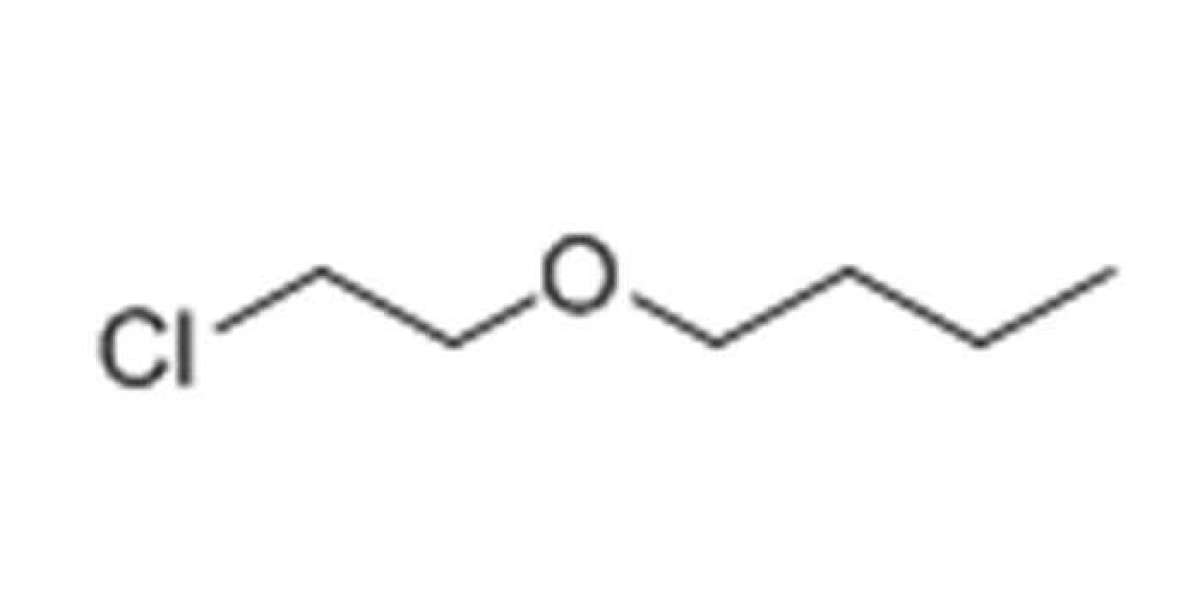
In this blog post, SACH BIOTECH will be discussing the process of extracting colorless liquid 2-Chloroethyl n-butyl ether. This chemical compound is commonly used in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. It is also used as a solvent and a chemical intermediate in the manufacturing of various products.
Before we dive into the extraction process, let's first understand what 2-Chloroethyl n-butyl ether is and its properties. This chemical compound is also known as Butyl 2-chloroethyl ether or BCE. It has a molecular formula of C6H13ClO and a molecular weight of 144.62 g/mol. BCE is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 173-174°C and a density of 0.91 g/cm3 at 20°C.
Now, let's move on to the extraction process. The extraction of BCE can be done using various methods, including distillation, liquid-liquid extraction, and solid-phase extraction. In this blog post, we will be discussing the liquid-liquid extraction method.
The liquid-liquid extraction method involves the use of two immiscible liquids, one of which is the solvent and the other is the target compound. In this case, the solvent used is usually an organic solvent such as diethyl ether, dichloromethane, or ethyl acetate. The target compound, BCE, is dissolved in the solvent, and the two liquids are mixed together. The mixture is then allowed to separate into two layers, with the BCE-containing layer being separated and collected.
Here are the steps involved in the liquid-liquid extraction of BCE:
Step 1: Preparation of the sample
The first step in the extraction process is to prepare the sample. This involves weighing the sample and dissolving it in the solvent. The amount of solvent used will depend on the solubility of the target compound in the solvent. It is important to ensure that the sample is completely dissolved in the solvent to ensure maximum extraction efficiency.
Step 2: Mixing the two liquids
Once the sample is dissolved in the solvent, the two liquids are mixed together. This can be done by shaking the mixture vigorously or by using a magnetic stirrer. The mixing process should be done for a sufficient amount of time to ensure that the two liquids are well mixed.

Step 3: Separation of the two layers
After the mixing process, the two liquids will separate into two layers. The BCE-containing layer will be the bottom layer, while the solvent layer will be the top layer. The separation can be done by allowing the mixture to settle for a sufficient amount of time or by using a separating funnel.
Step 4: Collection of the BCE-containing layer
Once the two layers have separated, the BCE-containing layer is collected and transferred to a clean container. The solvent layer can be discarded or reused for further extractions.
Step 5: Purification of the BCE-containing layer
The collected BCE-containing layer may contain impurities, which can be removed by further purification. This can be done by using techniques such as distillation or chromatography.
In conclusion, the liquid-liquid extraction method is an effective way to extract colorless liquid 2-Chloroethyl n-butyl ether. This method involves the use of two immiscible liquids, one of which is the solvent and the other is the target compound. The two liquids are mixed together, and the BCE-containing layer is separated and collected. The collected layer may be further purified to remove impurities. It is important to follow proper safety precautions when handling chemicals and to dispose of them properly.
https://www.hzsqchem.com/How-to-extract-colorless-liquid-2-Chloroethyl-n-butyl-ether.html