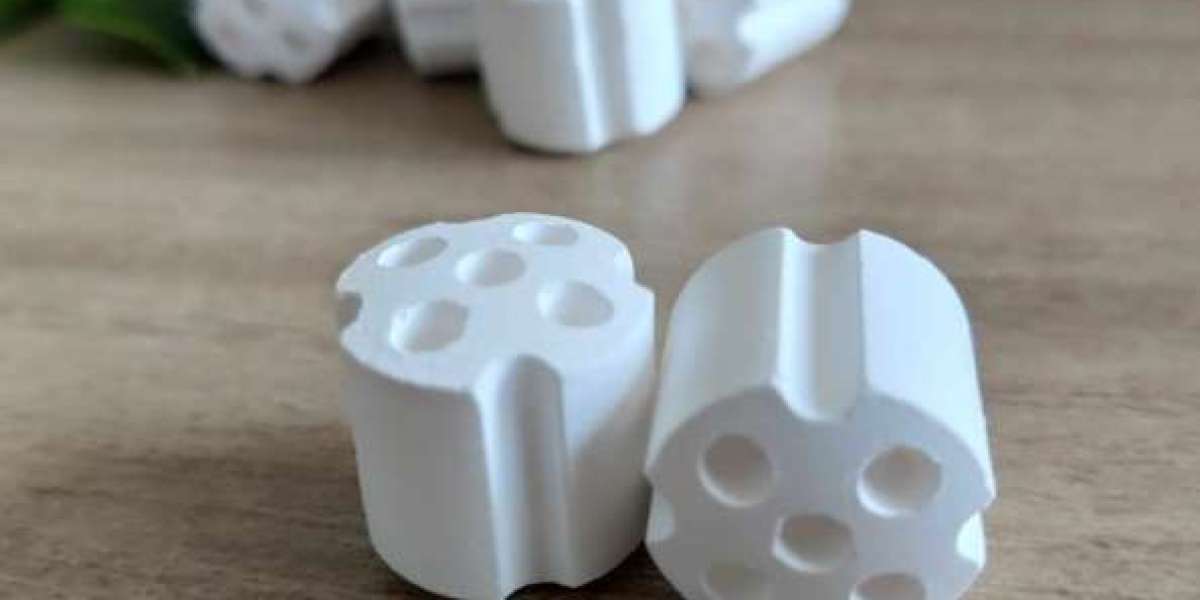
Hydrocarbon reforming is a critical process in the petrochemical industry, playing a vital role in converting hydrocarbons into more valuable products such as hydrogen, gasoline, and other fuels. At the heart of this process are catalyst carriers, which significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of reforming reactions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of hydrocarbon reforming catalyst carriers, their functions, types, and the factors that affect their performance.
What is Hydrocarbon Reforming?
The Reforming Process
Hydrocarbon reforming refers to a set of chemical processes that convert hydrocarbons into more useful products. The most common types of reforming include:
1. Steam Reforming: This process involves reacting hydrocarbons with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. It is widely used in hydrogen production for fuel cells and ammonia synthesis.
2. Catalytic Reforming: This process transforms naphtha into high-octane gasoline components and aromatic compounds. It typically involves the use of a catalyst to facilitate the reaction at elevated temperatures and pressures.
3. Dry Reforming: In this process, carbon dioxide is used alongside hydrocarbons to produce syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide), which can be further processed into fuels or chemicals.
Importance of Catalyst Carriers
Catalysts are substances that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. In hydrocarbon reforming, catalyst carriers provide a support structure for the active catalytic materials, enhancing their effectiveness and stability. The choice of catalyst carrier can significantly impact the overall efficiency of the reforming process.

The Role of Catalyst Carriers in Hydrocarbon Reforming
Enhancing Catalytic Activity
Catalyst carriers serve several essential functions in hydrocarbon reforming:
Support for Active Sites: Catalyst carriers provide a surface for the active catalytic materials to adhere to, increasing the available surface area for reactions. This is crucial for maximizing catalytic activity.
Thermal Stability: High temperatures are often required for reforming reactions. Catalyst carriers must withstand these conditions without degrading, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Mass Transfer: Effective mass transfer of reactants to the catalyst surface is vital for efficient reactions. The design and porosity of catalyst carriers can enhance the diffusion of reactants and products, improving overall reaction rates.
Selectivity: The choice of catalyst carrier can influence the selectivity of the reaction, determining the types and quantities of products formed. This is particularly important in processes like catalytic reforming, where the goal is to maximize high-octane gasoline production.
Types of Hydrocarbon Reforming Catalyst Carriers
1. Alumina-Based Carriers
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is one of the most commonly used catalyst carriers in hydrocarbon reforming. Its high surface area, thermal stability, and ability to support various catalytic metals make it an ideal choice. Alumina can be modified to enhance its properties, such as increasing its acidity or basicity, which can further improve catalytic performance.
2. Zeolite Carriers
Zeolites are microporous crystalline materials that offer unique properties for catalytic applications. Their well-defined pore structures allow for selective adsorption and diffusion of reactants, making them suitable for processes requiring high selectivity. Zeolite-based catalyst carriers are often used in catalytic reforming to produce high-octane gasoline.
3. Carbon-Based Carriers
Carbon-based materials, such as activated carbon and carbon nanotubes, are gaining popularity as catalyst carriers due to their high surface area and tunable properties. They can provide excellent thermal stability and facilitate mass transfer, making them suitable for various reforming processes.
4. Metal Oxide Carriers
Metal oxides, such as zirconia (ZrO₂) and titania (TiO₂), are also used as catalyst carriers in hydrocarbon reforming. These materials can enhance the catalytic activity of supported metals and improve the overall stability of the catalyst system.

Factors Affecting Catalyst Carrier Performance
1. Surface Area and Porosity
The surface area and porosity of catalyst carriers are critical factors that influence their performance. A higher surface area allows for more active sites for catalytic reactions, while appropriate porosity ensures efficient mass transfer of reactants and products. The design and synthesis of catalyst carriers must consider these parameters to optimize performance.
2. Thermal Stability
Hydrocarbon reforming processes often operate at high temperatures, making thermal stability a crucial factor for catalyst carriers. Materials that can withstand extreme conditions without significant degradation will ensure consistent catalytic performance over time.
3. Chemical Compatibility
The chemical environment in which the catalyst operates can affect the performance of the carrier. Catalyst carriers must be chemically compatible with the reactants and products to avoid unwanted reactions that could lead to deactivation or reduced efficiency.
4. Metal Support Interaction
The interaction between the catalyst metal and the carrier can significantly influence catalytic activity. Strong metal-support interactions can enhance the dispersion of active sites, improving overall performance. Conversely, weak interactions may lead to sintering or agglomeration of the catalyst, reducing effectiveness.
Recent Advances in Catalyst Carrier Technology
1. Nanostructured Carriers
Recent research has focused on developing nanostructured catalyst carriers that offer enhanced surface area and improved mass transfer properties. These materials can provide more active sites for reactions and improve overall catalytic performance.
2. Tailored Carriers
Advancements in material science have enabled the design of tailored catalyst carriers with specific properties for targeted applications. By modifying the composition and structure of carriers, researchers can optimize their performance for particular reforming processes.
3. Hybrid Carriers
Hybrid catalyst carriers, which combine different materials, are being explored to leverage the advantages of each component. For example, combining zeolites with metal oxides can enhance both catalytic activity and selectivity, leading to improved reforming outcomes.

Conclusion
Hydrocarbon reforming catalyst carriers play a crucial role in the efficiency and effectiveness of reforming processes. By providing support for active catalytic materials, enhancing thermal stability, and facilitating mass transfer, these carriers significantly impact the overall performance of hydrocarbon reforming systems. Understanding the various types of catalyst carriers, the factors affecting their performance, and recent advancements in technology is essential for optimizing hydrocarbon reforming processes. As the demand for cleaner and more efficient energy sources continues to grow, the development of innovative catalyst carriers will be vital in advancing the petrochemical industry and supporting sustainable energy solutions.
Yixing Winner Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer in producing catalysts and their ceramic carriers, ceramic glove formers, and other industrial ceramics.
Welcome to inquiry if you need to know more about hydrocarbon reforming catalyst carriers details or order wholesale.