Secondary steam reforming is a pivotal process in industries like hydrogen production, ammonia synthesis, and petrochemical production. This process involves the catalytic conversion of methane and other hydrocarbons into synthesis gas (syngas), primarily composed of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). Secondary steam reforming catalyst supports are an essential component in optimizing this conversion, improving efficiency, and ensuring the sustainability of the entire process. In this article, we will explore the advantages and applications of secondary steam reforming catalyst support, emphasizing their role in enhancing reactor performance and driving technological advancements in various industrial sectors.
Understanding the Role of Catalyst Supports in Secondary Steam Reforming
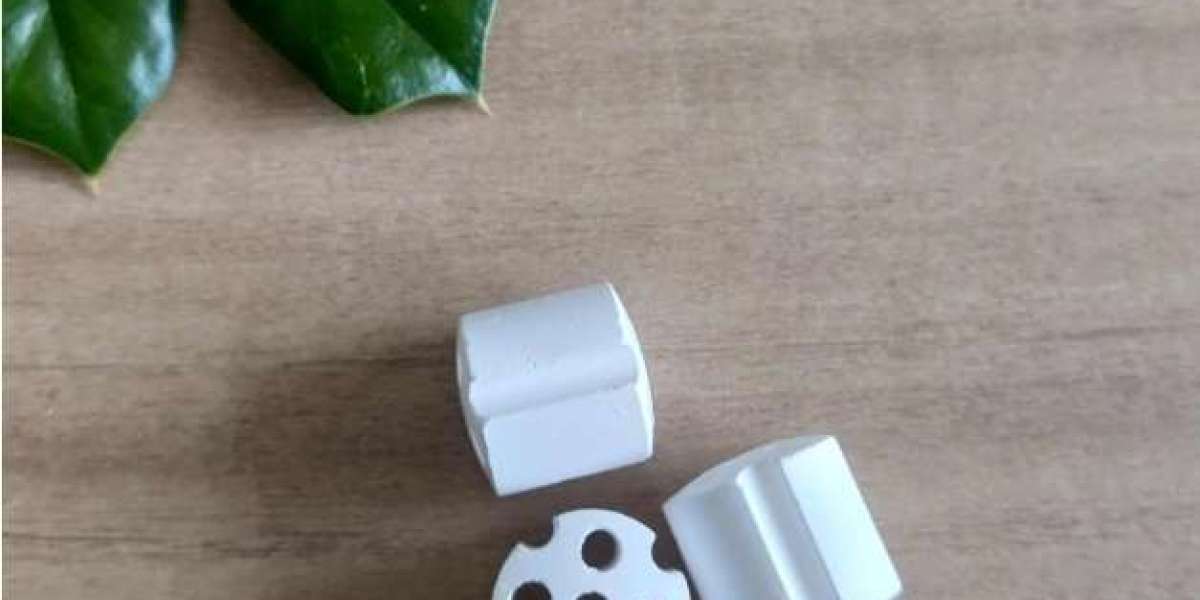
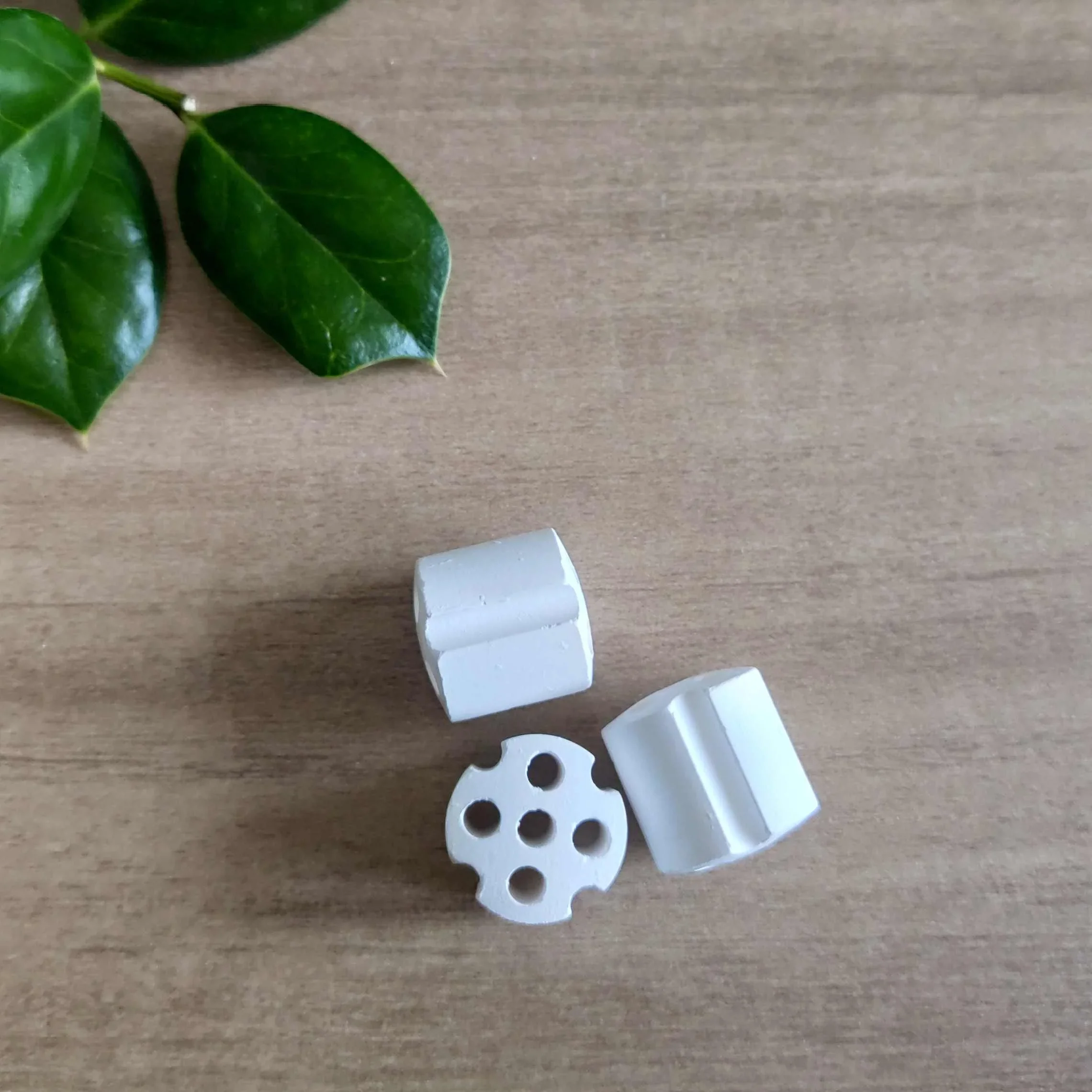
In secondary steam reforming, a catalyst is used to accelerate the chemical reactions that transform methane and steam into syngas. The catalyst support, typically a solid material such as alumina, silica, or a metal oxide, serves as a framework for the catalyst, providing a surface for the active catalytic sites. The catalyst support not only facilitates the dispersion of the active phase (such as nickel or platinum) but also helps improve the thermal stability and resistance to deactivation, which are crucial for the long-term efficiency of the reforming process.
The secondary steam reforming process generally follows the primary reforming stage, where methane reacts with steam in the presence of a catalyst at high temperatures. The secondary reforming takes place in a separate reactor, usually in the presence of air or oxygen, to further convert the remaining methane into additional syngas.

![]()
Advantages of Secondary Steam Reforming Catalyst Support
1. Enhanced Catalyst Performance
One of the primary advantages of using catalyst supports in secondary steam reforming is the significant improvement in catalyst performance. By providing a high surface area and uniform distribution of active sites, catalyst supports enhance the efficiency of the chemical reactions. This leads to a higher yield of syngas and a reduction in the overall energy consumption required for the reforming process. The improved dispersion of the catalyst also ensures that the active sites are fully utilized, optimizing the conversion of methane into useful products.
2. Increased Thermal Stability
Secondary steam reforming processes typically occur at temperatures between 800°C and 1000°C, which can cause significant thermal stress on the catalyst. Catalyst supports provide thermal stability to the active catalyst phase, preventing the sintering (clumping together) of catalyst particles and maintaining their activity. Materials like alumina or zirconia are commonly used as catalyst supports due to their high thermal resistance. These supports help prevent the degradation of the catalyst during prolonged operation, leading to a longer catalyst life and reduced replacement costs.
3. Enhanced Resistance to Poisoning and Deactivation
Catalysts in secondary steam reforming are susceptible to poisoning by impurities such as sulfur compounds, chlorine, and carbon deposits. Catalyst supports contribute to the overall resistance of the catalyst to these poisons by providing a physical barrier that prevents the poisons from directly interacting with the active sites. Furthermore, by offering a larger surface area for dispersion, catalyst supports allow for a more even distribution of the active phase, which minimizes the likelihood of deactivation due to localized buildup of poisons.
4. Better Control over Reaction Kinetics
The performance of secondary steam reforming catalysts is heavily influenced by reaction kinetics, including the adsorption and desorption of reactants and products. Catalyst supports help optimize these kinetics by ensuring a uniform distribution of active sites and providing a more stable environment for the reaction to occur. This allows for more precise control over the reaction rates, which is particularly important for large-scale industrial applications. By improving the kinetics of the process, catalyst supports also contribute to higher production rates and improved process economics.
5. Cost-Efficiency
Using catalyst supports can result in cost savings in several ways. First, by improving the efficiency of the reaction, catalyst supports help reduce the amount of expensive catalyst required for a given process. Additionally, their ability to extend the life of the catalyst and reduce the frequency of catalyst replacements leads to lower operating and maintenance costs. The cost-effectiveness of catalyst supports is particularly significant in large-scale industrial processes, where the scale of operation can lead to substantial savings over time.
Applications of Secondary Steam Reforming Catalyst Support
Secondary steam reforming catalyst supports are integral to various industrial applications, most notably in the production of hydrogen and ammonia. Below are some of the key applications where catalyst supports play a critical role:
1. Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen is an essential feedstock for numerous industries, including petroleum refining, chemical manufacturing, and fuel cell technology. Secondary steam reforming is one of the primary methods of producing hydrogen from natural gas. The use of catalyst supports in this process improves the efficiency of hydrogen production by optimizing the conversion of methane into hydrogen. As the demand for hydrogen grows, particularly in the context of green energy solutions like fuel cells and hydrogen-powered vehicles, the role of secondary steam reforming catalyst supports becomes increasingly vital in meeting this demand.
2. Ammonia Synthesis
Ammonia is a key component in the production of fertilizers, and the process of ammonia synthesis relies heavily on the production of syngas via secondary steam reforming. In ammonia plants, the synthesis gas is converted into ammonia through the Haber-Bosch process, which requires an efficient and reliable syngas supply. By enhancing the efficiency of the secondary steam reforming process, catalyst supports help ensure a stable and high-quality syngas feedstock for ammonia production. This, in turn, contributes to the overall productivity and cost-effectiveness of ammonia synthesis.
3. Petrochemical Industry
The petrochemical industry relies on syngas as a feedstock for the production of chemicals such as methanol, acetic acid, and synthetic fuels. Secondary steam reforming plays a key role in generating syngas from methane or natural gas, and the use of catalyst supports enhances the overall efficiency and economics of the process. By improving the yield of syngas and reducing the energy required for reforming, catalyst supports contribute to the competitiveness and sustainability of the petrochemical industry.
4. Environmental Applications
As the global focus shifts toward sustainability and reducing carbon emissions, secondary steam reforming plays a role in producing cleaner fuels and chemicals. The efficiency improvements enabled by catalyst supports help minimize energy consumption, reducing the carbon footprint of industrial processes. Additionally, secondary steam reforming can be integrated with carbon capture technologies to further reduce emissions, making it a valuable tool in the pursuit of greener industrial practices.

Conclusion
Secondary steam reforming catalyst supports are essential components in the optimization of the steam reforming process, improving the efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of catalyst systems. By enhancing catalyst performance, increasing thermal stability, and extending catalyst life, these supports provide numerous benefits that are crucial for industrial applications such as hydrogen production, ammonia synthesis, and petrochemical manufacturing. As industries continue to seek more efficient and sustainable methods of production, the importance of catalyst supports in secondary steam reforming will only continue to grow, driving innovation and enhancing the performance of vital chemical processes.